Malware (Malicious Software) is “software that is specifically designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to a computer system.” It can harm us in many ways – both directly when it infects our devices and through major attacks on the businesses and institutions we use.
Ahh… But I have anti-virus, a VPN and a password manager and I never click on those links in suspicious e-mails and SMS messages . So I’m safe aren’t I ?
Wrong! Both the delivery of malware and the malware itself have become very sophisticated. AI has made it easier to deceive people and the weakest link is …As always – You and I –
Here’s an analogy (sort of)
Imagine a scenario where company reps come to give an estimate for an air con installation in a posh private house. One of them sees door keys lying on a shelf near the back door. He sneakily unlocks it and contacts a gang of villains who turn up later and walk right in, disabling the alarm system in the process. They carefully go through the house checking personal documents, investments, passwords, and bank account details, being sure they leave everything undisturbed. They then hide in a wardrobe and turn the alarm back on, so the owner is unaware of the intrusion. Then the villains watch the owner’s behaviour: Ah – bingo! He trades stocks and shares using portal X, The owner is security conscious and has not recorded his username and password anywhere, however the gang can see him typing in the credentials and they make a log of his keystrokes. The gang notes that the owner also has some cryptocurrency and is doing some shady stuff with his tax returns, as well as having an affair with a lady down the road. They relay all this information back to their head office. Sometime later the owner discovers that his stock trades have been made on a fake platform and are worthless, while his real investments have been siphoned off to goodness knows where. His savings have gone and he receives a letter saying that his tax evasion and affair will be made public for all to see unless he pays a huge sum in crypto.
The important thing about this tale is that it is a multi-stage process. It is an ..
Infection chain
1. The bad guys (commonly called “Threat Actors” find a lapse in security, then let the others in. This is the “loading” and “delivery” process.
2. The theft, the “payload” is stealthy and unseen.
3. The loot is “exfiltrated” – sent off to be analysed and used to extort money, or sold to other criminal parties.
Delivery: This is where the weakest link plays its part. Some malware uses more than one delivery method, and some “delivery” boys can deliver more than one Malware payload.
There seems to be a trend these days to initiate widespread attacks rather than creating new malware. On the other hand, AI can create or modify existing malware so that it dynamically adapts itself to evade detection by traditional Anti Virus software.
Delivery routes
The most common method of delivery in 2024 was through “Maladvertisements” (see below) https://www.cisecurity.org/insights/blog/top-10-malware-q4-2024
Phishing
“the fraudulent practice of sending emails or other messages purporting to be from reputable companies in order to induce individuals to reveal personal information, such as passwords and credit card numbers.“
Here’s a recent SMS example:
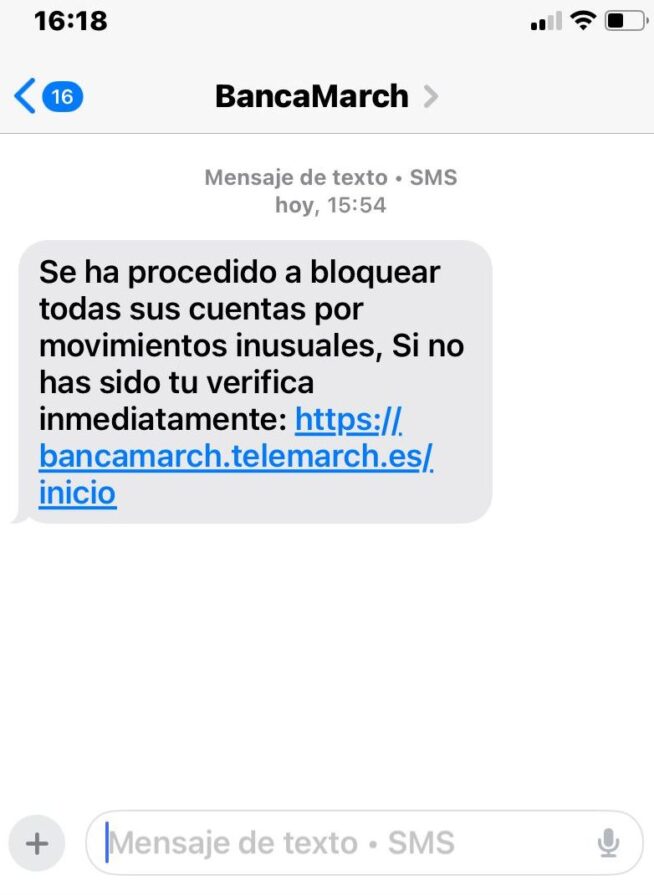
This is the classical type of delivery, of which we are all aware.
However, there are no giveaway spelling mistakes these days since the tricksters use translation tools and AI.
Note how the URL you are asked to click on looks formal and legitimate.
Spearphishing: A type of phishing campaign that targets a specific person or group and often includes information known to be of interest to the target, such as current events or financial documents. In 2024 online trading portals were being targeted. https://www.sharecast.com/promoted/economic_news/dark-web-scams-targeting-online-traders-in-2024.html
“….cybercrooks pose themselves as any legitimate trading platform or brokerage. Such fraudsters send traders emails or messages that look like official letters in order to make the trader click on malicious links or disclose sensitive information“…”The hackers look for weak points either in the software or in the infrastructure of the platforms where access to users’ accounts becomes possible. In addition, if traders use weak or repeated passwords across many platforms, it’s way easier for scammers to get into these accounts. After gaining access, they can manipulate the trades, withdraw funds, or sell the account details to other criminals.”
Spearphishing with Infected Excel file attachments on e-mails – e.g. a CEOs e-mail account has been stolen and an underling receives an e-mail from his boss asking him to check the attached Excel spreadsheet… PDF files can also carry infections.
For the tech savvy, here are “Examples of Phishing Attacks and How to Effectively Analyze Them”
Fake Software
Fake software includes infected apps for phones, tablets and PCs. Always get your apps from reputable sites, however, infected apps can be found even in reputable App stores; “Kaspersky’s report challenges the assumption that official app stores are entirely secure. The cybersecurity firm recently identified SparkCat, a sophisticated screenshot-stealing malware that bypassed Apple App Store security measures and was also found on Google Play. In total, 20 infected apps were discovered across both platforms, reinforcing the need for vigilance when downloading apps.”
https://ibsintelligence.com/ibsi-news/banking-data-theft-on-smartphones-surge-196-are-you-at-risk/
Fake Browser updates
These attacks are a type of social engineering and malware delivery method where attackers trick users into downloading and installing malicious software disguised as a legitimate browser update. Several threat groups use this fake update browser lure as part of their attack” These are delivered on hacked or faked websites. Fake browser update attacks typically involve:
- A compromised Website – Attackers distribute malware using compromised resources, injecting malicious JavaScript into vulnerable sites to fingerprint hosts, perform eligibility checks, and display fake update pages.
- Fake Update Page – A customized fake update page tricks users into downloading a malicious payload.
- Delivery – The malware is commonly delivered via drive-by downloads. These occur when a user visits the compromised or malicious website, unintentionally downloading malicious software.
- Payload – The payload is typically a JavaScript file within a ZIP archive. The malicious JavaScript acts as a downloader, delivering additional malware.”
(Note: A drive-by download can take advantage of an app, operating system, or web browser that contains security flaws due to unsuccessful updates or lack of updates. Unlike many other types of cyberattack, a drive-by doesn’t rely on the user to do anything to actively enable the attack. https://www.kaspersky.com/resource-center/definitions/drive-by-download )
Adware/Malvertisements
Hackers are now buying ad space on Google Search and other search engines as a means to trick users into installing malware. One of the ways in which they do this is by impersonating popular brands. So far, we’ve seen hackers impersonating Amazon, USPS, CCleaner, Notepad++ and other household names. However, Facebook and Microsoft have remained the most impersonated brands since 2020 “ https://www.tomsguide.com/news/hackers-have-found-an-insidious-way-to-attack-you-with-malware-dont-fall-for-this
Some Malvertisement ads lead the user to Fake CAPTCHA pages which encourage the user to command Windows to download the Malware! https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/malicious-ads-push-lumma-infostealer-via-fake-captcha-pages
Malicious ads on Torrent sites Many torrent websites rely on ad revenue to maintain their platforms, and these ads can sometimes be malicious. Even if you’re not downloading a torrent, clicking on a misleading or malicious ad can expose your device to malware.“
Infected Torrent videos
https://www.bitdefender.com/en-us/blog/hotforsecurity/torrents-pirated-tv-shows-lumma-stealer The film you are downloading is packaged with malware “ In most situations, the uploader offers an episode of an anticipated TV show that hasn’t aired yet, hoping to attract people actively looking for it.” ..The download size looks right, and the usual naming scheme is respected. A lower resolution version of the film is packaged with a malware file (e.g. SCR file) with the same name.
Malicious tips on Chat platforms
e.g. on Discord (which is used by gamers) – the bad guys dupe users into downloading infected software. Similarly: StackOverflow: a Q and A website for computer programmers has been used this way. https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/cybercriminals-pose-as-helpful-stack-overflow-users-to-push-malware
Fake Messaging Apps
There are fake WhatsApp apps, so get yours from the official site. Phishing messages are also spread on this and other messaging platforms.
Fake and compromised “useful” websites
e.g. Fake File conversion services – e.g. You upload a Word document to get it converted to a PDF. Then download the PDF. On a fake site, they may “scrape” personal data from the file and/or infect the downloaded file with malware.
Fake Reddit – which you stumble across when searching for tech support advice. The content on these fake pages is written in such a way that it resembles an actual Reddit thread. They start with a question asking for a specific tool and then to trick potential victims further, a fake Reddit user replies to the thread with a download link and another fake user thanks them for doing so. This helps build trust with victims and makes them believe that the download link is legitimate and not malicious. https://www.tomsguide.com/computing/online-security/hackers-have-created-hundreds-of-fake-reddit-sites-to-spread-info-stealing-malware
Youtube channels with links to malware, which is often hidden in links in the comments. https://www.infosecurity-magazine.com/news/youtube-channels-hacked
Snail Mail
Chris received a printed letter from “NatWest” a couple of years ago. This asked her to go online to confirm her personal credentials. Recently snail mail letters have been used to attempt a ransomware scam. https://www.scworld.com/news/cybercriminals-go-old-school-with-snail-mail-ransomware-scheme
Home smart appliances . The Internet of Things “IOT”
IoT malware differs from traditional computer viruses in several key ways. These malicious programs are often designed to operate on devices with limited processing power and memory, making them more challenging to detect and remove. They can also spread rapidly across networks of connected devices, creating large-scale botnets capable of launching devastating distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks.
Baby monitors, wif fi security, refigerators, many peoples’ routers are not secure. We have previously mentioned modern cars and their internet connections. There’s a lot of potential here!
What is Malware, and what can it do?
Malware (Malicious Software) is “software that is specifically designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to a computer system.” These are complex, sophisticated and powerful programs which are capable of circumventing computer security. Some have overlapping capabilities and actions and are configurable, even by non-technical people. https://any.run/cybersecurity-blog/malware-trends-2024
- Stealers – A type of trojan which steals sensitive information and sends it off,
- Loaders– are used during the initial stage of multi-stage malware attacks to load other malware
- Remote access Trojans (RAT) also called remote administration tools, enable unauthorized clandestine remote control of a target’s computer system.
- Ransomware – this locks computer data until a fee is paid.
- Keyloggers– records keystrokes,
- Trojans – masquerade as benign software,
- Miners – use a PC to mine crypto,
- Adware – unwanted ads,
- Backdoor – bypass the standard authentication and security systems
The popular Lumma Stealer follows a “malware-as-a-service model”, Lumma Stealer is accessible to anyone with the financial means to purchase a subscription. This accessibility has contributed to the malware’s widespread adoption. There are three subscription plans, each providing a different range of features for hackers to use. https://any.run/malware-trends/lumma
A few months ago Chris saw a demonstration of a RAT – Remote access Trojan which controls the infected computer remotely. The njRATcan activate the webcam, log keystrokes, manipulate files and execute programs. It can steal passwords and cryptocurrency and start up each time the computer is turned on. It is configurable and there are many online tutorials on how to use it, It can hide from Antivirus and infect external hard drives plugged in by USB. It is one of the most popular Rats in the world! https://any.run/malware-trends/njrat
Banking data theft is on the up. It tripled on smartphones in 2024. https://techround.co.uk/news/banking-data-theft-smartphones-tripled-2024/
Who is spreading this Malware?
No one can be sure because the “Threat Actors” keep themselves hidden, though some groups can be localised to Russia. In the past, most of the emphasis has been on political and corporate attacks carried out by State sponsored groups: North Korea, Russia and China. But, like scamming, this activity is also big business for entrepreneurs!.
- Criminal gangs – like the pig butchers moving into pastures new.
- Disaffected employees – some modern malware can be implemented by non techies.
- Competitors : Interestingly, China’s Deepseek AI was attacked. The Chinese say it was from locations in the US where its main competitors are located!… https://www.scmp.com/news/china/politics/article/3296765/cyberattack-deepseek-including-brute-force-assault-started-us-chinese-state-media
- Rogue hackers – just because they can. e.g. the case of the Internet outage of Orange.es. When asked why they hacked the account, the hacker says they did it for the “lulz,” or in other words, for the laughs. https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/hacker-hijacks-orange-spain-ripe-account-to-cause-bgp-havoc
Note malware is available for free on the Dark Web for any would be Threat Actor
Why am I not completely safe if I use security tools like Antivirus, VPN ?
- Antivirus: Only works with known viruses. Just think about the lack of natural immunity to COVID in humans. The same goes for malware in computers. In addition some malware is configured to hide itself from Antivirus programs.
- VPN: These help in some circumstances, but not others! https://www.aura.com/learn/does-a-vpn-protect-you-from-viruses
- Two Factor Authentication: This helps, but again is not 100% bullet-proof https://www.aura.com/learn/does-two-factor-authentication-prevent-hacking
- What about Password Managers?: They are under attack! “hackers have adjusted their malicious campaigns to shift their focus towards password managers. And it makes sense. Why would a hacker put their time and effort into stealing a target’s login credentials to just one service when they could steal all their login credentials? Why steal a key to open just one door when you can take the master key and access everything?” https://mashable.com/article/password-managers-cyberattacks-malware
Tips
- Keep your system (Windows, Android, Apple iOs), Browser, anti Virus and anti malware up to date.
- Do not re-use passwords, make them difficult to guess, or use a password manager.
- Use two-step biometric authentication when you can
- Don’t install unnecessary apps. Get them from reputable App stores.
- Have more than one device separated by air for different functions.
e.g. Do your banking, stock trading etc on a PC which is NOT used for general messing about on the Internet. If you use Torrent sites, use a dedicated device (e.g. an old PC loaded up with Linux) and scan the downloaded files for malware. https://linuxsecurity.com/features/the-three-best-tools-you-need-to-scan-your-linux-system-for-malware
What does 2025 hold for us?
Time will tell! https://www.pandasecurity.com/en/mediacenter/cybercrime-in-2025-what-to-look-out-for/
